XoligoTM – xylooligosaccharide (Feed Grade)
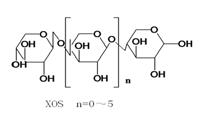
Chemical Structure
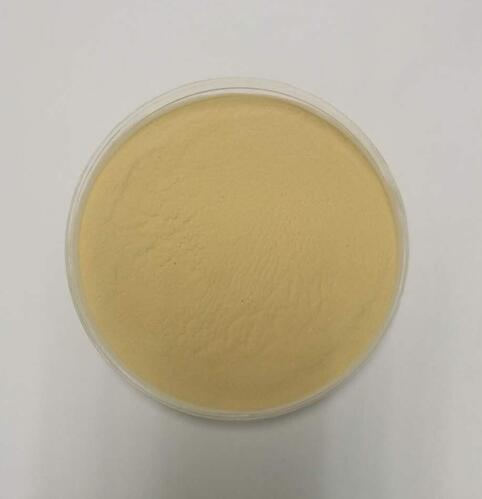
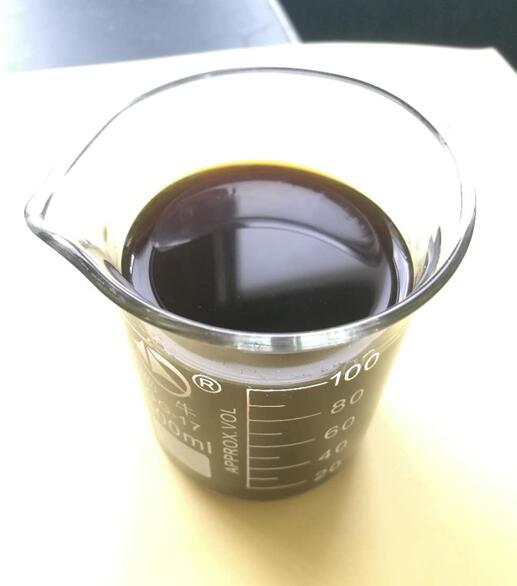
Component
The usage (All the usage methods can be adjusted according to the customers)
Advantages
XoligoTM synbiotics
XOS can be used together with probiotics and enzymes as follows:


- XoligoTM – xylooligosaccharide is one of the functional xylans formed by 2 to 7 xylose molecules

Component
- The content of xylooligosaccharide is over 35% (solid) or 25% (liquid) with xylobiose, xylotriose and xylotetraose as the main components.
- Brown powder or liquid.
- The organic texture of XOS is similar to that of the surface receptors of the epithelial cells, so XOS can bond to the exogenous lectin proteins of pathogenic bacteria, which prevents the adhesion of the pathogenic bacteria to the epithelia cells.
-
Super Bifidus-Factor – Bifidobacterium takes the advantage of XOS as the food to proliferate fast:
- Barrier: The lectin produced by bifidobacterium can bond to the glycoprotein of the epithelial cells, which prevents the adhesion of the pathogenic bacteria to the intestine epithelia.
- Destruction: The extralcellular glycosidase produced by bifidobacterium can degrade the polysaccharide receptors on the surface epithelial cells which could be combined by the pathogenic bacteria and endotoxin, so that to prevent the adhesion of pathogenic bacteria and endotoxin to the intestine epithelia.
- Acid production: XOS can be degraded to VFAs by bifidobacterium, resulting in the decrease of the intestinal pH, which is negative to the survival of the pathogenic bacteria.
- Nutrition: A lot of trophic factors can be produced by bifidobacterium after the ingestion of XOS, including VB1, VB2, VB6, VB12, niacin and folic acid, etc..
- Improve the health of animals
- Improve the production of animals
- Improve the feed efficiency
-
Pig
- Piglets
- Pregnant swine
- Perinatal and lactating sows
- Growing-finishing pig
-
Poultry
- Broilers
- Laying hens
The usage (All the usage methods can be adjusted according to the customers)
-
Pig
- Nursery pigs
- Pregnant swine
- Perinatal and lactating sows.
- Growing-finishing pigs
- Doses: 200 g/T for the perinatal and lactating and growing-finishing pigs; 150-200 g/T for nursery pigs.
-
Poultry
- Broilers
- Laying hens
Advantages
- High content of effective constituents (xylobiose, xylotriose, xylotetraose), ≥32%.
- Low usage dose and powerful effects.
- Good stability (heat-, acid- and enzyme-resisting).
XoligoTM synbiotics
XOS can be used together with probiotics and enzymes as follows:
- XOS (35%) + lactobacillus (≥1×109 CFU/g)
- XOS (35%) + bacillus (2×1010 CFU/g)
- XOS (35%) + glucose oxidase (10000 U/g)
- XOS (35%) + lactobacillus (≥1×109 CFU/g) + bacillus (2×1010 CFU/g)
- XOS (35%) + lactobacillus (≥1×109 CFU/g) + glucose oxidase (10000 U/g)
- PS: All the synbiotics can be adjusted according to the customers.


